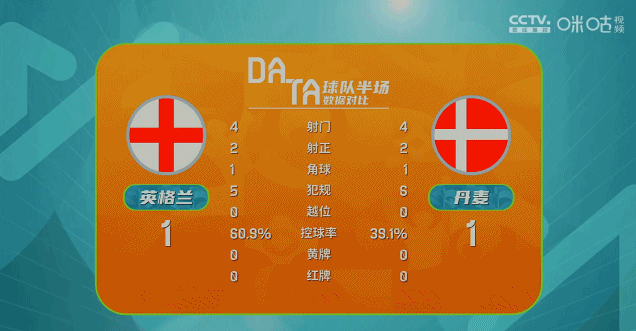
专科体育类和普通类能同时报吗
Title: Exploring the Differences Between Sports Science and General Specialization
In the realm of higher education, two distinct paths often emerge for those passionate about sports: specialized degrees in sports science and more general degrees in various disciplines. Let's delve into the nuances of these pathways to understand their differences and potential career trajectories.
Sports Science Specialization:
Sports science is a multidisciplinary field that encompasses aspects of physiology, biomechanics, psychology, nutrition, and exercise prescription, among others. Students pursuing a degree in sports science typically undergo rigorous training in these areas, with a focus on understanding the scientific principles behind athletic performance and injury prevention.
Curriculum Highlights:
1.
Exercise Physiology:
Students learn about the physiological responses and adaptations to exercise, including topics such as energy systems, cardiovascular function, and muscular physiology.2.
Biomechanics:
This aspect explores the mechanics of human movement, analyzing factors such as force, motion, and torque to optimize athletic performance and reduce the risk of injury.3.
Nutrition:
Understanding the role of nutrition in sports performance and recovery is crucial. Courses cover topics such as macronutrient and micronutrient requirements, hydration strategies, and dietary supplements.4.
Psychology:
Sports psychology delves into the psychological factors that influence athletic performance, including motivation, stress management, goal setting, and mental skills training.5.
Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation:
Students learn techniques for preventing sportsrelated injuries and strategies for rehabilitating athletes after injury, including therapeutic exercises and modalities.Career Opportunities:
1.
Strength and Conditioning Coach:
Designing and implementing exercise programs to improve athletic performance and reduce the risk of injury.2.
Sports Nutritionist:
Providing personalized nutrition plans to optimize athletes' performance and recovery.3.
Sports Scientist:
Conducting research to enhance understanding of sports performance and contribute to evidencebased practice in the field.4.
Athletic Trainer:
Providing onsite medical care and rehabilitation for sportsrelated injuries.5.
Coach or Sport Consultant:
Applying scientific principles to enhance coaching strategies and athlete development.General Specialization:
General specialization refers to pursuing a degree in a traditional academic discipline, such as biology, psychology, nutrition, or kinesiology, with a broader focus that may not necessarily center solely on sportsrelated topics.
Curriculum Highlights:
1.
Biology:
Courses in biology cover fundamental principles of life sciences, including cell biology, genetics, anatomy, and physiology.2.
Psychology:
General psychology courses explore various aspects of human behavior, cognition, and emotion, providing a foundation for understanding mental processes.3.
Nutrition:
Studying nutrition involves learning about the role of nutrients in human health and disease, dietary guidelines, and food science.4.
Kinesiology:
Kinesiology encompasses the study of human movement and physical activity, including biomechanics, exercise physiology, and motor control.Career Opportunities:
1.
Medical Professional:
Pursuing careers in medicine, physical therapy, or occupational therapy to work with athletes or individuals seeking to improve their physical health.2.
Researcher:
Conducting scientific research in areas such as biology, psychology, or nutrition, with potential applications to sports performance or general health.3.
Educator:
Teaching courses in biology, psychology, or related fields at educational institutions.4.
Health and Wellness Consultant:
Providing guidance on nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle modifications to promote overall wellbeing.5.
Public Health Specialist:
Working in public health organizations to address community health issues and promote healthy behaviors.Guidance and Recommendations:
1.
Passion and Interest:
Consider your interests and career goals when choosing between sports science and general specialization. If you're deeply passionate about sports and exercise, sports science may offer a more tailored educational experience.2.
Career Flexibility:
While sports science degrees provide specialized knowledge, general specialization can offer a broader skill set that may be applicable across various industries and career paths.3.
Practical Experience:
Seek opportunities for handson experience, such as internships, research projects, or volunteer work, to complement your academic studies and enhance your employability.4.
Continuing Education:
Regardless of your chosen path, staying updated on the latest research and advancements in your field is essential for professional growth and development.5.
Networking:
Build connections with professionals in your desired field through networking events, conferences, and professional organizations to gain insights and opportunities for career advancement.In conclusion, both sports science specialization and general specialization offer unique pathways for individuals interested in the intersection of sports, health, and science. By understanding the differences between these educational tracks and considering your personal interests and career aspirations, you can make informed decisions to pursue a rewarding and fulfilling career in your chosen field.
欧洲杯直播
MORE>-
01-15曼联中国官网,连接红魔世界,引领足球文化新风尚
-
01-15逆风翻盘!武磊替补登场智勇并举,关键时刻再显超级前锋本色
-
01-15王者回归,巴塞罗那在西班牙国王杯中重燃辉煌,战术解析与球队深度剖析
-
01-14黄潜挑战红魔,比利亚雷亚尔的崛起与曼联的应对策略
-
01-14莱昂纳多·迪巴拉,足球巨星的东方华丽转站——鲁能新篇章
-
01-14足球场上的眼泪,内马尔的真情瞬间,揭示运动员的心灵独白
-
01-14一球定乾坤,足球中的智慧与团队力量
-
01-14传奇教练佩特莱斯库,坚韧不拔的足球灵魂与罗马神话的缔造者
-
01-14骑士与热火,一场篮球对决中的勇气与智慧
-
01-13俄罗斯与乌拉圭,足球盛宴中的对话,历史、战术与未来的碰撞
-
01-13中国足球,面对叙利亚,我们能学到什么?一场学习与成长的世界杯预选赛
-
01-12揭秘足球传奇,吉安妮娜·马拉多纳,她的故事与影响力
-
01-11NBA总决赛赛程大揭秘,冠军争夺战的激动瞬间即将开启!
-
01-11解锁创新未来,凯尔安德森——推动科技与生活的魔法师
-
01-11燃烧的战火,火箭VS勇士录像深度解析,引领你走进NBA争霸的新篇章
- 搜索
- 最近发表
-
- 探秘南美洲荣耀,阿根廷世界杯2022名单深度解析及未来展望
- 光影交织,永恒传奇——奥斯卡献礼科比,篮球巨星的不朽荣光与人生哲学
- 羽翼飞扬,奥运舞台——探究伦敦奥运会羽毛球魅力与竞技深度
- 揭秘足球盛宴,探索世界杯网站的全面指南
- 揭秘2021年世俱杯,足球盛宴背后的中国崛起与全球影响
- 巴黎奥运会,体育盛宴的曲折路途——取消与转型的项目深度解析
- 篮球经济学大考,NBA新赛季的工资帽风云,谁是真正的领头羊?
- 揭秘NBA总决赛重播的魅力,深度解析与精彩回顾
- 詹姆斯,35岁的荣耀与传奇,岁月沉淀下的篮球巨星生日献礼
- 曼联中国官网,连接红魔世界,引领足球文化新风尚
- 菲尔·杰克逊,篮球场上的魔术师与禅意教练
- 逆风翻盘!武磊替补登场智勇并举,关键时刻再显超级前锋本色
- 王者回归,巴塞罗那在西班牙国王杯中重燃辉煌,战术解析与球队深度剖析
- 德甲焦点对决,多特蒙德与马拉加的碰撞,揭示足球战术新趋势
- 国安与拜仁,足球赛场上的中国荣耀与欧洲霸主的碰撞
- 黄潜挑战红魔,比利亚雷亚尔的崛起与曼联的应对策略
- 莱昂纳多·迪巴拉,足球巨星的东方华丽转站——鲁能新篇章
- 足球场上的眼泪,内马尔的真情瞬间,揭示运动员的心灵独白
- 荣耀之舞,重温86年世界杯决赛的激情与传奇
- 瑞典与斯洛伐克,和谐共处的北欧邻居——一场独特的欧盟文化对话
- 标签列表
-
- 2024欧洲杯比赛时间 (22)
- 2024年欧洲杯预选赛 (24)
- 2024欧洲杯百度百科 (19)
- 欧洲杯一场比赛打多久 (11)
- 怎么看欧洲杯直播 (10)
- 2024欧洲杯杯 (10)
- 欧洲杯2024在哪个国家 (13)
- 欧洲杯为什么2023年举办 (10)
- 欧洲杯为什么没有直播 (12)
- 欧洲杯共多少场比赛 (11)
- 在哪里可以看欧洲杯预选赛 (18)
- 2024欧洲杯主办城市 (15)
- 欧洲杯一场比赛时间多长 (11)
- 欧洲杯参赛球队有几支 (10)
- 欧洲杯有多少只球队参加 (11)
- 欧洲杯多久举行一次 (10)
- 欧洲杯在哪个国家举行2024 (11)
- 欧洲杯一共多少球队 (10)
- 欧洲杯为什么这么受欢迎 (10)
- 为什么欧洲杯看不了 (11)
- 欧洲杯为什么没有中国 (10)
- 欧洲杯决赛怎么看 (11)
- 直播软件 (12)
- 直播吧官网 (13)
- 直播吧 (14)